Autodesk Inventor uses a unified Autodesk material and appearance database, which is used for the entire Autodesk component group. In its database, Woodwork for Inventor add-on uses items from the aforesaid database, complementing this information with data necessary to ensure functioning of Woodwork for Inventor. Such a synchronized coexistence of the two databases requires attention and its management is rather complicated. The actual design process faces intense change of material nomenclature; therefore, it is difficult to create and maintain new synchronized items in Woodwork for Inventor and Autodesk Inventor databases. For this reason, in the construction process with Woodwork for Inventor, materials are assigned in two stages:
| 1. | A general Woodwork for Inventor material (also known as material group) is assigned to parts. This assignment defines the type of material. For example, board, profile banding or desktop, etc. The material also defines the function of the part to which the material is assigned. For example, facade part of the first colour, facade part of the second colour, body, etc. |
| 2. | At the last construction stage, the general material code, name and appearance can be replaced with the specific material code, name and appearance. |
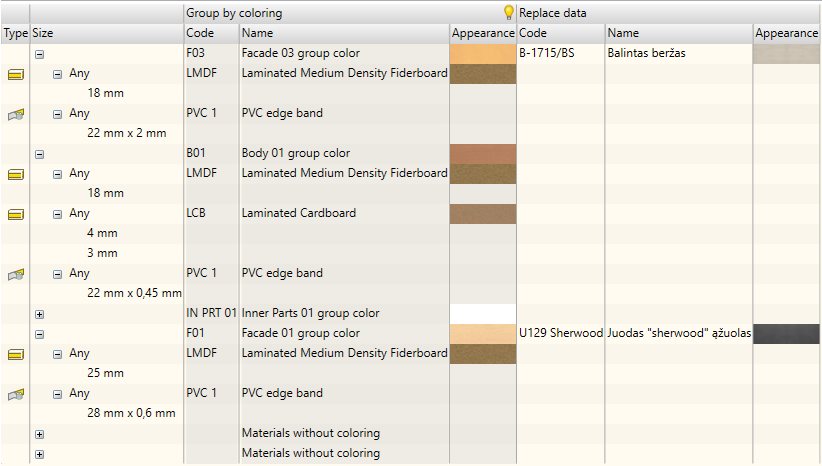
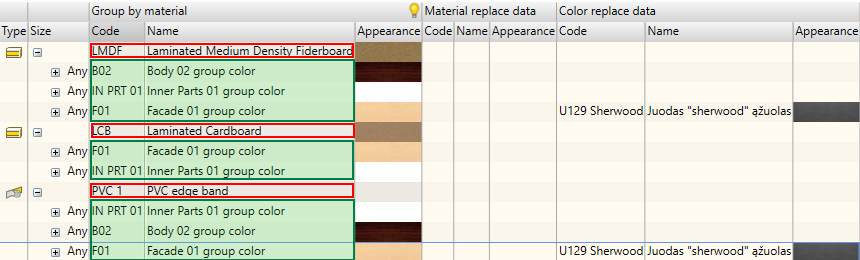
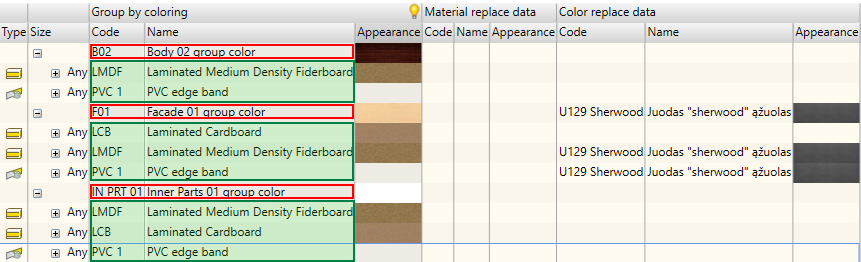
When performing the replacement command, Woodwork for Inventor generates a material summary for the model. Materials in the summary are presented based on the Woodwork for Inventor material concept. Here, they are grouped into regular materials and materials that have colours.
Regular materials include:
Description of such materials includes the following:
Materials that have colours include:
Description of such materials includes the following:
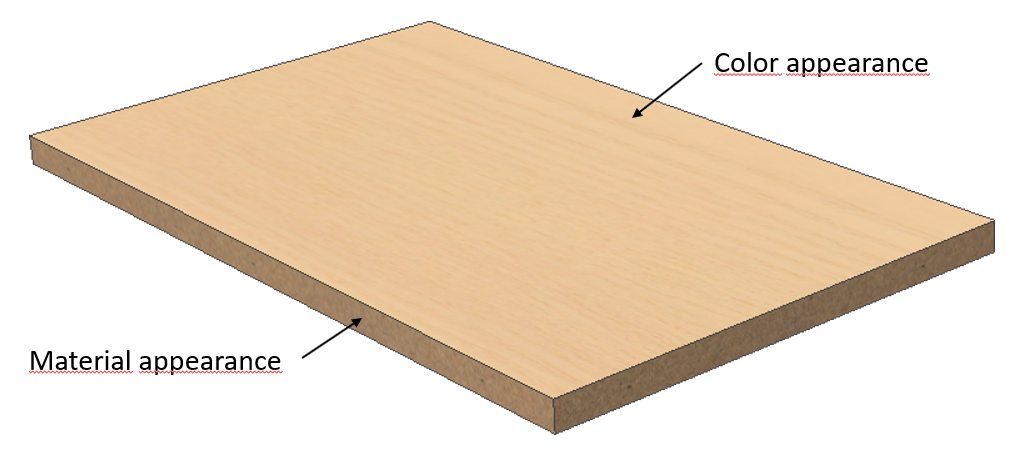 Example of a material that has colour. In this case, explanation of appearances of a laminated board.
The materials are additionally grouped according to geometric parameters. Examples include board thickness, edge band width and thickness, profile cross-section dimensions, etc. Geometric parameters that define the material depend on the material type. Below is a table showing material types and the corresponding parameters:
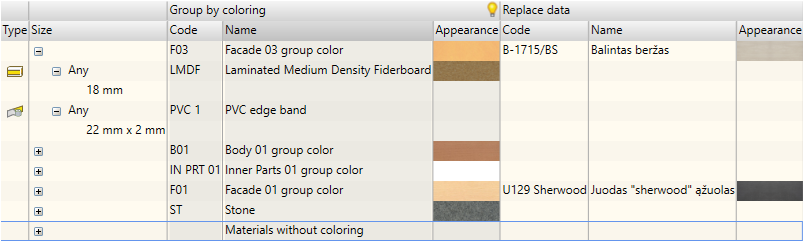
If the material used for the part has the same code, name, appearance, colour, colour code, colour appearance (if the material has colour) and geometric parameters, then it is the same material.
The example above show how Woodwork for Inventor analyses the model and materials used for parts. It presents these materials in the summary grouped by colour, material and geometric parameters.
|
On the right side of the replacement desktop, you will find data columns, where you can enter the replacement values, which will be used with all data export points that involve the appropriate material. This information is used by BOM Generator, Auto Plot and CNC Output.
The user can change the data in the following ways:
1. By entering the desired material code and name into the table using the keyboard. To enter the name, place the cursor on the cell and press F2 on the keyboard. The appearance can be changed by double-clicking on the appearance cell. Once the dialogue window opens, select the desired appearance image file.
2. By selecting the item from the linked MS Excel worksheet. In this case, the replacement values will be imported from the selected row of MS Excel worksheet. To make the change, click on MS Excel icon that is displayed in the replacement cell. You can additionally change the appearance image. For information on linking MS Excel files, please read here.
The user can choose from several ways of displaying the replacement data.
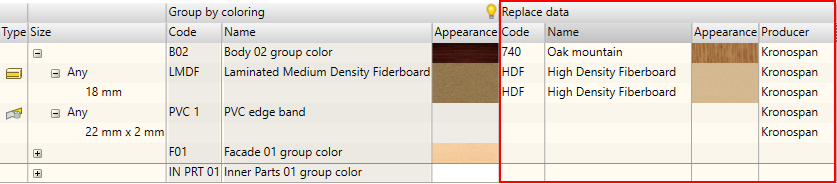
In the above figure, you can see the display summary for the replacement data. This is a compact and convenient option. After making changes to the colour line, the user will automatically make colour changes to all items that belong to the tree branch at hand. Changes to materials result in the relevant material replacements.
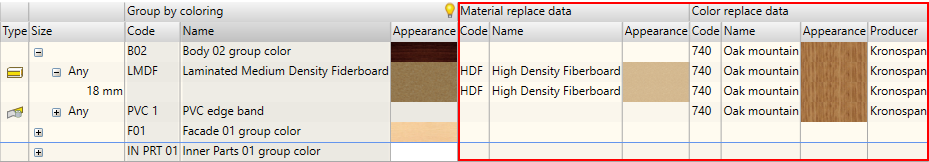
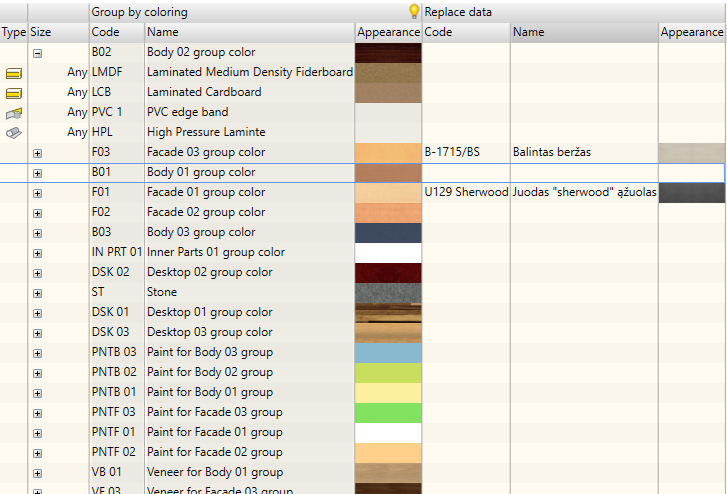
In the above figure, you can see the extended display of the replacement data. This option should be used if the company uses different material codes for materials with different colours. This situation usually occurs where ERP systems are used. Every item characterized by different dimensions, materials needs to be registered as a separate material even if it has the same colour. In this case, it is easier to work with an extended data form. Information about management of data display can be found here.
|
As mentioned above, the user can change material codes, names and appearance. In other words, virtually replace a general material with the specific one. Such replacements can often be applied to other pieces of furniture being designed. All such replacements can be saved as replacement configuration. When constructing another piece of furniture, you will simply have to apply this configuration. Having found the material mentioned in the replacement in the material summary for the model, Woodwork for Inventor add-on will automatically make the replacement. This way the user can memorise the most popular and tested material or colour replacements and apply them in one go without separately changing data for each general material. The user can create as many configurations as he wants. The user can also remove such configurations. Only Default configuration installed with Woodwork for Inventor cannot be removed. Using these configurations and the same geometry of the piece of furniture, the user can quickly produce information necessary to begin the production with different materials.
Woodwork for Inventor also allows creating replacement configurations for materials that are not included in the material summary of the specific model. Replacement configurations can be created for general materials that are included in Woodwork for Inventor material database. In this case, the material will not be grouped by geometry. Where geometric parameters of the material are provided, any value will be assigned to the material, which means that the material can be of Any Size. This is because general materials included in Woodwork for Inventor database have no information as to their size as long as they are not assigned to the specific parts in the model. In the replacement window, you can choose different display options that allow viewing only the materials included in the model or all materials included in Woodwork for Inventor database and the completed model. Using a replacement configuration where replacement combinations are provided for general materials from Woodwork for Inventor database, changes will be made to all parts in the model regardless of their geometric parameters. For example, let’s say that we have a registered configuration where the colour of laminated board F01; Facade 01 Group colour code has to be replaced with R4647C; Alder. Once the configuration is applied, parts made of boards with the thickness of 25 mm and 18 mm whose colour is F01, will be subject to the same change, i.e. R4647C; Alder colour. On the other hand, if such replacement was registered for boards with the thickness of 18 mm, the material of a board with the thickness of 25 mm will remain unchanged.
The most recent replacement configuration opened for editing will be treated as the active replacement configuration. It can be opened from the configuration tool bar. Please note that data of the active replacement configuration will be used in all processes of Woodwork for Inventor. Data of the active replacement configuration are used for the following commands:
|
The user can keep material and colour lists in MS Excel files. Values from this file can be copied to the replacement cell.
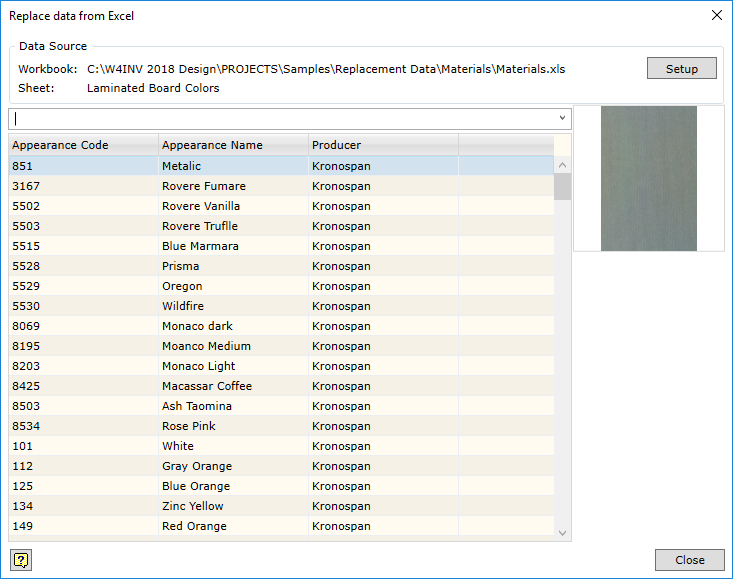
Linking with MS Excel worksheet Replacement data are a regular MS Excel worksheet, where the data are presented in freely arranged columns (first figure from the top). If the given replacement configuration was linked to MS Excel worksheet, data from the worksheet will be displayed in the selection window (second figure from the top). One worksheet can be linked to all material types or each type can be linked to a separate data worksheet. The item to which the worksheet is linked depends on the location of the cursor in the link dialog box when MS Excel file to be linked is selected. Below are the examples of linking each type to separate data worksheets.
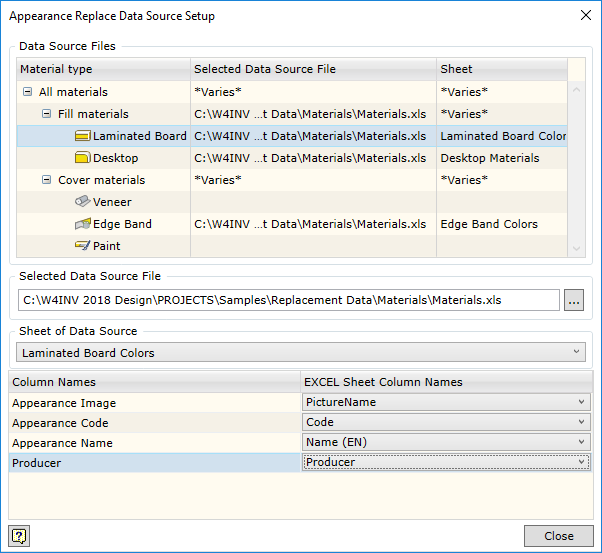
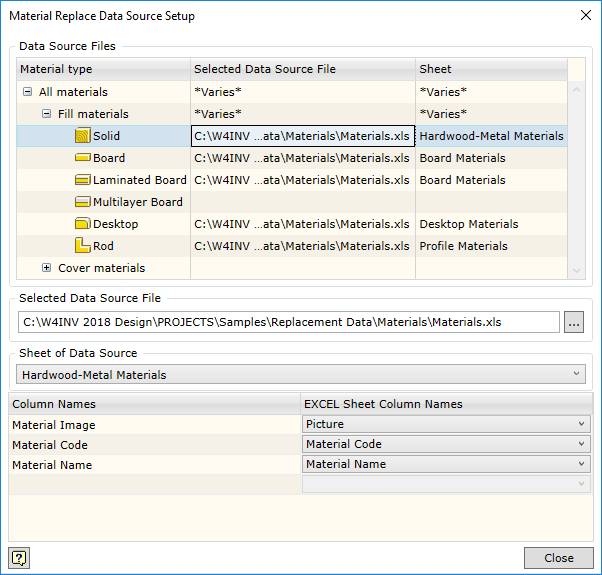
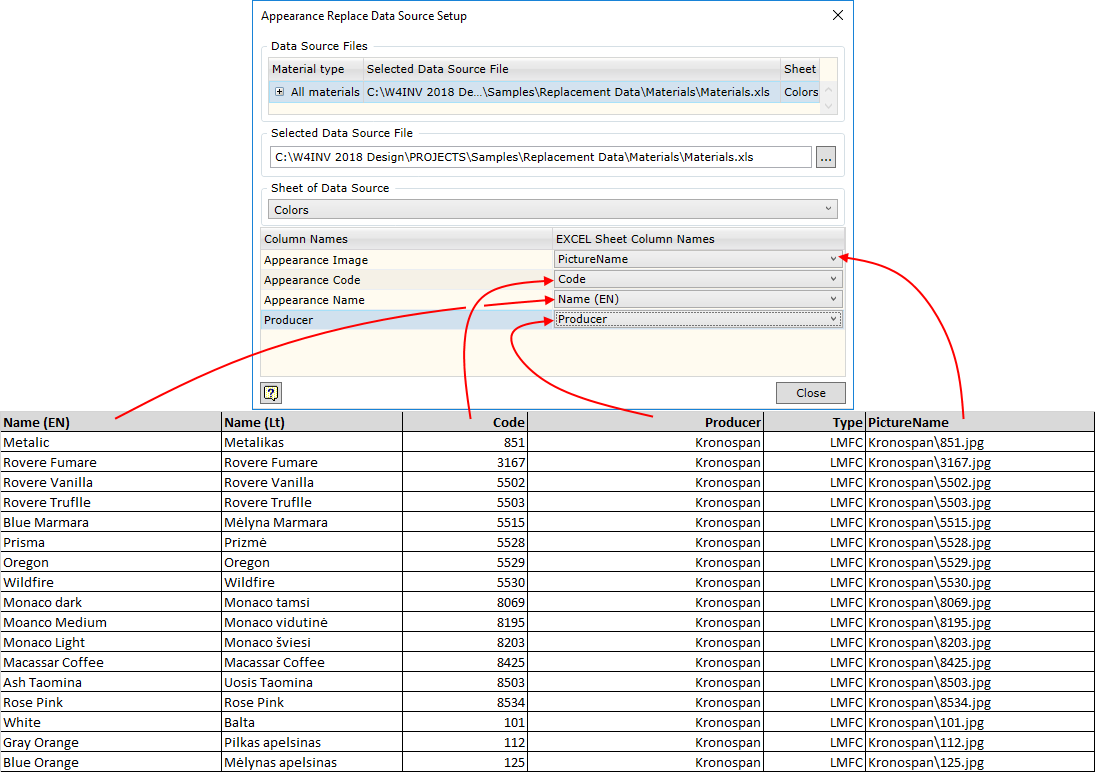
The link dialogue box is opened by clicking on MS Excel icon (figure below). As mentioned above, if the current configuration has already been linked, a window with values imported from MS Excel file will be displayed. Otherwise this window will be empty. MS Excel worksheet can be linked by clicking the Setup button in this window. It should be kept in mind that linking for colours is made when the link dialogue box is opened via Colour replace data (figure below). To create the link for materials, the dialogue box should be opened via Material replace data.

Entering additional data for the material. When setting up the link, three fields are always given:
If the user needs more fields, he can add a new field and link it to the field in MS Excel worksheet. In the example above, you can see how Producer field is added. This way you can specify additional material characteristics such as fire safety of the material, material names in additional languages, etc. Values of these fields can be opened in specifications and drawings by means of keywords.
Synchronous linking of material and colour. In certain cases, it is necessary to link a colour to a different material from the specification. This usually happens when using ERP systems. Below is the appropriate example, where you can see how colour generates a different material code.
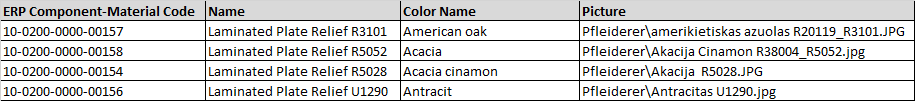
If you want the colour selection result in change to the material code or vice versus, you have to link the material and the colour to the same worksheet. In this case, selecting a colour will result in the appropriate change in the material cell and vice versus.
Registering appearance images. The user can change not only the digital information, but also the appearance of the material or colour. To do this, MS Excel file has to contain a data column specifying the path to the image file that will be used to change the appearance. Image files have to be located in the same catalogue as MS Excel file or they can be stored in subdirectory located in the main catalogue that contains MS Excel file.
|
Only code and name appear in purchased components. Similarly, as in the case of materials, here the user can change a code and a name. This way the same confirmat screw in the assembly model can be ordered using different codes from different suppliers.
Changes to the purchased components can be made only in the BOM generator dialog box. Click here to see a detailed description of how the Woodwork for Inventor replacement command works.
|
After performing replacements of field values, modified field values will be exported to BOM specifications via the keywords. For example, Item.FillWorkpiece.Material.colour.Code keyword exports a modified workpiece colour (if any). However, there may be cases when you have to indicate, in the BOM specification, the field values that were obtained during the reading of the CAD model by the Woodwork for Inventor BOM generator. In other words, original field values are required. In this case for each item that defines the material and has a replacement value, there is an option of extracting an original value obtained during the reading of the model. In this case, you can use the Original prefix for each such modified field.
For example, we need to know what an original colour code of a given material is. For this purpose, you need to enter the Material.Original.colour.Code keyword in the table description. Or, let’s assume a material name is required: Material.Original.colour.Name.
In case a replacement was not performed, an original name corresponds to the replaced name.
|